What Part Of The Brain Controls Sadness
Abstruse
Exercise you like science fiction? Take you heard of, or are you lot even a fan of, the famous "Star Wars" series? To summarize, there are rebels, emperors, princesses, robots, and many more than fabled creatures. There is as well a power source chosen "The Force." It is used by the Jedi (the good ones) but besides by the dark side (the evil ones). Only the nighttime side uses the destructive ability of "The Force," which is based on negative emotions such as fearfulness, anger, jealousy, or detest. A Jedi masters "The Force" and uses it for knowledge and defence force by learning to control his emotions. Our inquiry besides looks at emotions and how to control them. Nosotros know that in our milky way too, we have more success when nosotros can control our feelings. Therefore, nosotros want to observe the brain regions responsible for allowing us to deal with our emotions and to help those children struggling with decision-making negative emotions.
Imagine walking downward the school hall thinking about your adjacent lesson. Suddenly, your best friend jumps out from a dark corner, correct in front of yous, wearing a light-headed mask and scaring y'all. This trick that was played on you lot immediately led to a reaction of your body. Y'all can feel your centre beating and maybe you only screamed out loudly. A few seconds later though, you lot recognize your friend and detect there is no real threat. Y'all may fifty-fifty start laughing most the joke. This is an example of how a person can react to an emotional state of affairs. Information technology also shows how our mind processes a situation using different clues. Emotions are feelings that (ane) are acquired by situations that are meaningful or of import to you, (2) are something you feel or show through your body language, and (3) may compete with other of import things [1]. In our example, the scary joke gave you the impression of existence attacked, and it is important to you lot to stay unharmed. Your beating middle and the screaming is the reaction of your body. While you are scared and your commencement intention might exist to run away quickly, you besides noticed that this was simply your friend playing a joke on you. Being scared and knowing someone is your friend are two different clues that might compete with each other in your brain. One clue tells you lot to run away in order to stay unharmed, and the other tells you to stay with someone y'all like (competing reactions). Within a separate second, you make a choice near which emotion yous find important and which emotion you lot choose to control or suppress completely. Overall, people tend to cull to decrease negative emotions (acrimony, sadness, or fright) and increase positive emotions (happiness, love, and joyfulness). Changing or controlling your feelings is an activeness we call " emotion regulation ." The way that you command and change your emotions is called your "emotion regulation strategy." Looking at data from many people, scientists were able to evidence that the manner you regulate your emotions influences how yous experience, just it also affects the people around you [1]. For example, if you have difficulties decision-making your emotions when being angry you may terminate upwards blasphemous, punching, or fifty-fifty bullying the people effectually yous. This is no fun for them either. Therefore, successful emotion processing and regulation is very of import for humans. In fact, emotion regulation difficulties are a office of many mental health bug in children, teenagers, and adults.
Using an MRI Camera for Studying the Brain
The way the brain processes and regulates emotions tin can be studied using a technique called magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An MRI scanner looks similar a big tunnel (see Figure 1A). Actually, it is merely a very fancy camera that is able to take images of all the parts within your body. For example, an MRI camera can take an image of the basic in your leg, of your chirapsia centre, or of the organ we are interested in – the encephalon. Nosotros can use the MRI camera to expect at the structure (shape and size) of the brain. When nosotros desire to see how the encephalon works, then we can use an MRI camera to look at brain function. Just as y'all demand more food when you do sports, your brain also needs more free energy when it becomes agile, simply instead of food it needs oxygen. Therefore, when a specific region in the brain is hard at piece of work, it will get more oxygen transported to it by the bloodstream. We call this claret oxygen-rich. Oxygen-rich claret gives unlike signals to the MRI camera compared with blood that has less oxygen. Using this noesis, researchers tin create an image of both the brain'south structure and function. With special figurer programs, we can brand pictures like the ones in Figure 1B. One of the nigh amazing things is that the MRI photographic camera can take pictures of your brain at work without fifty-fifty touching y'all! Only there are some challenges for people who have part in research studies using an MRI. Ii of the biggest challenges are that (1) you accept to stay super however while the pictures are taken or they get blurry (for an explanation, come across Figure 2) and (2) you accept to protect your ears against the noise. Big cameras such as an MRI can be quite loud, which is why y'all need to habiliment special headphones. Staying nevertheless can be practiced with fun games, such equally the freezing game, where you accept to stay still like an ice statue. If you desire to know more than and see what MRI experiments involving young children look like, you tin watch the post-obit video (http://www.jove.com/video/1309/making-mr-imaging-child-due south-play-pediatric-neuroimaging-protocol [two]).
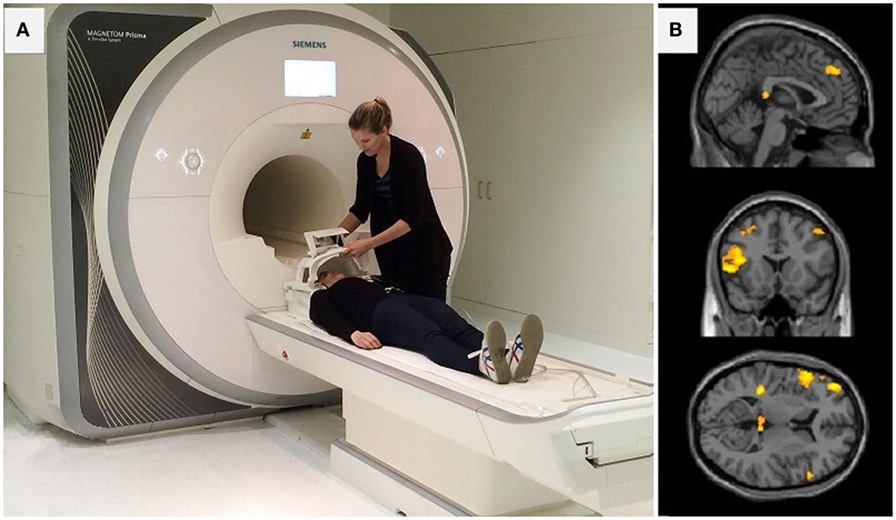
- Figure 1
- A. Two of our research team members showing you lot an MRI camera and how it is used. B. Unlike views of a child'southward brain every bit taken by an MRI camera. The areas that are colored yellow are of import for emotion processing and regulation.
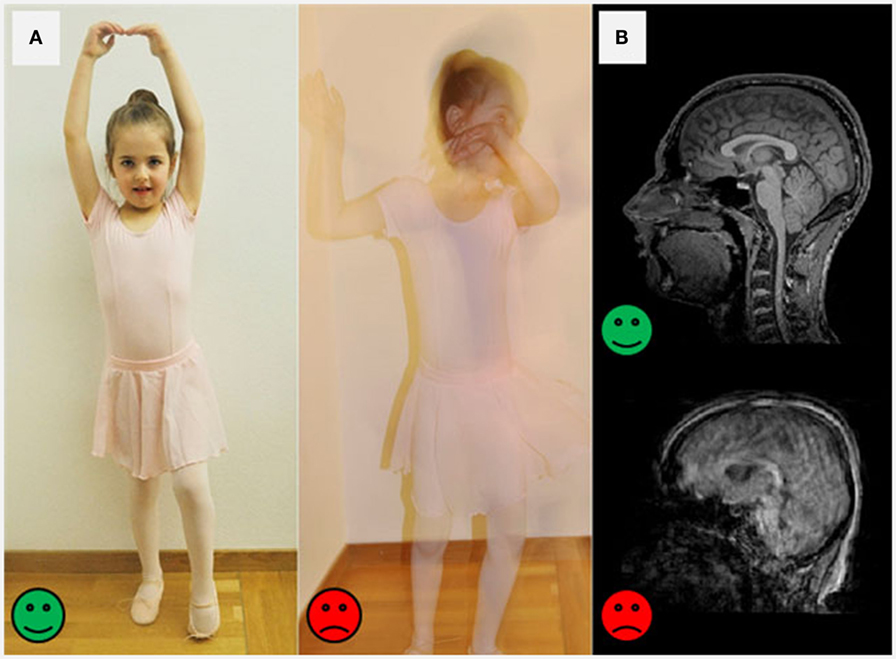
- Figure 2
- Why staying nevertheless during an MRI session is important: A. A picture show taken by a regular photographic camera can exist very sharp when the person is standing super still (green happy face up). But when the person is moving a lot, the motion-picture show becomes blurry (red sad face up). B. The aforementioned is true when taking encephalon pictures. The pictures can plough out super sharp when the person stays still (green happy face up) or blurry and hard for scientists to read for when the person wiggles around (red sad face).
What Does the Encephalon Look Similar While Processing and Regulating Emotions?
At present, in the outset department, you learned about feelings, which scientists call emotions. You heard that emotions tin lead to a reaction in your body. You also know that sometimes nosotros experience several emotions at once and that sometimes it is necessary to control a feeling and not to act on it. This procedure is called emotion regulation. In the second section, y'all learned how an MRI camera works and how it can be used to take images of the structure and function of the brain. In the next section, we want to combine these two things and talk most the parts of the brain that are responsible for processing and regulating emotion.
Using MRI cameras, scientists have shown that emotions are processed by many different areas of the brain. There is non but one place that is responsible for processing an emotion. Several encephalon regions piece of work together as a squad. This is why scientists say that emotions are candy by a network of encephalon regions. A network of brain regions that process emotions is called an emotion processing network (see Effigy 3). Let united states name some of those brain regions that are activated by emotions. They are the amygdala, the prefrontal cortex, the cingulate cortex, the hippocampus, and the basal ganglia [iii]. Fancy names, but it is not these names you need to remember. What is of import to understand is that at that place are many brain regions involved during emotion processing. All the unlike regions have their ain job and they all work together to identify and control an emotion. The amygdala, for example, is a tiny role of the brain (it has the shape and size of an almond), and information technology is responsible for handling both positive and negative information. The amygdala is especially of import when we experience the emotion of fear. Another region of the emotion processing network is the prefrontal cortex, which is named later on its location: in the front end of the encephalon. The prefrontal cortex is like a command middle, helping to guide our deportment, and therefore, this expanse is likewise involved during emotion regulation. Both the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are office of the emotion network. Only like good friends, these different encephalon regions stay in touch and communicate oft with each other. For example, the amygdala (the emotion center) can detect an important fearful effect and send that information to the prefrontal cortex (the control center). The prefrontal cortex gets the message that at that place is something scary happening. If necessary, this command eye at the front of your head sends commands to other brain regions telling them to motility your torso and run abroad. To sum information technology up, many brain regions work together to process and react to an emotional situation (see Figure 3).
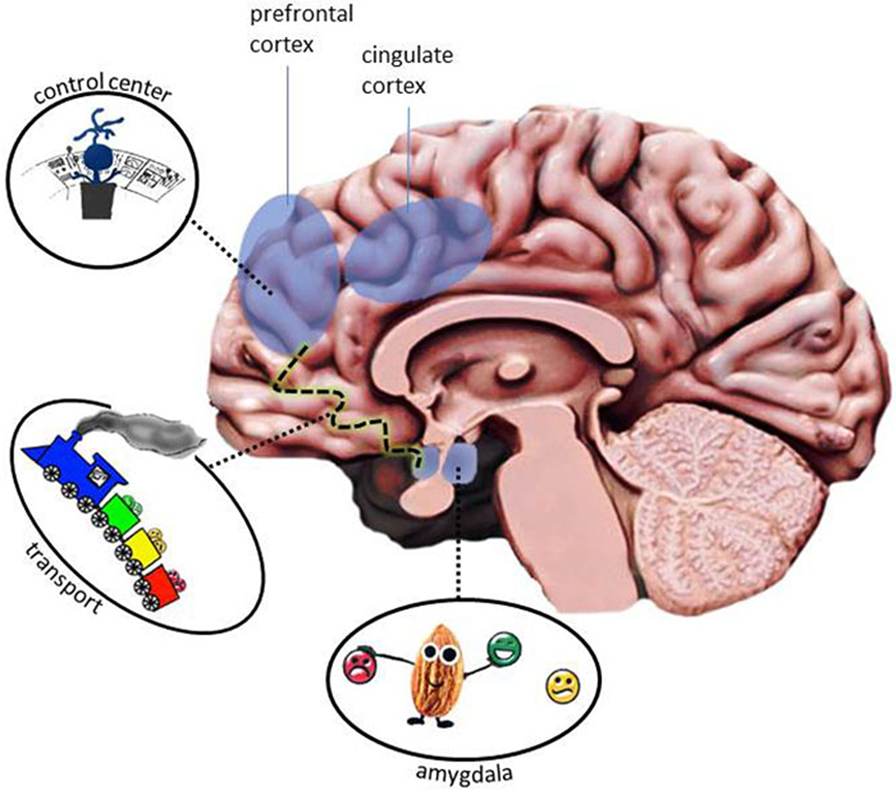
- Effigy 3 - The emotion processing network includes several areas of the brain.
- Some of these areas are shown here shaded in blue and you lot can see their different jobs: the amygdala (almond) recognizes and sorts the emotions before transporting them to other areas. In the picture, this transportation is visualized past a train driving along the dotted track line to the well-nigh frontal role of the brain. Once the information arrives there, the prefrontal cortex and the cingulate cortex human activity as a command heart (petty man backside desk), deciding what has to be done next with the incoming emotions. Many areas piece of work together to process an emotion! (illustration by Menks).
What Happens in the Brain When Emotion Processing Fails?
By now, you empathize that feelings are complicated and that emotions are represented and processed by many regions in the brain. You lot also remember that successful emotion regulation is important for a persons' well-being and central for the people around them. As mentioned before, information technology can exist really difficult to be around people that are constantly cursing, hitting, or bullying the people effectually them because they cannot command their negative emotions. Unfortunately, some children struggle more than than others with their emotions. Imagine you lot have a classmate named Jamie, who has problems with regulating emotions, specially acrimony and fear. At present picture that you brand a giddy joke with Jamie, but instead of laughing, Jamie gets very upset and perhaps even starts fighting with you. This is an example of someone who has emotion regulation difficulties. Such difficulties in handling emotions can oft exist observed in very aggressive (often fighting and bullying) and antisocial (breaking rules) teenagers. Research studies have shown that these teenagers cannot always successfully identify their emotions. Information technology tin too be very difficult for these children to command their emotions, like in the example of Jamie. This is not fun for y'all, if you get a victim of Jamie when he wants to fight you. But it is also non fun for Jamie, who might be expelled from school for his behavior. It is no fun either for his parents or the people around him. You can see that many individuals are afflicted by Jamie's difficulties controlling his emotions.
Considering we are interested in how the brain processes and regulates emotions, we exercise a lot of work with children who can successfully handle their emotions. We besides invite children who struggle with emotion processing and regulation to encounter whether their encephalon structure and office looks any different from the children who practise not have trouble with emotion processing. So far, there take been several pocket-sized studies, suggesting that there are differences in encephalon office and construction in children with aggressive beliefs [four]. Merely, equally our MRI section describes, in that location are challenges when doing research studies with younger participants. For example, information technology is very hard for children to stay very still while the MRI takes pictures (Effigy 2A). Because of this, nigh studies accept a very small-scale number of participants, and the results are non as clear. A method called " meta-assay " helps to summarize the information from all of these very important pocket-size studies. Meta-analysis takes the results of many studies and combines them into ane large finding. For example, we take combined all small studies washed and then far in children and teenagers with aggressive behavior [five]. While each study had a maximum size of about twoscore participants, combining all of them into one meta-analysis immune us to await at over 500 children at in one case. Past doing so, we were able to show changes in both brain construction and encephalon activity (office) in the emotion processing network in aggressive teenagers (Effigy 3).
May "The Forcefulness" be with Yous!
To summarize, emotions are feelings that are processed by a team of encephalon regions. Emotion processing is a complicated process, which sometimes does not piece of work so well. Difficulties with emotion processing and regulation are found in children and teenagers with very ambitious and antisocial behavior. Using structural and functional neuroimaging techniques, we showed that areas of the emotion processing network of the brain are unlike in the youths with aggressive behavior. Luckily, the encephalon has the power to change and adapt, especially when people are still young. The more than nosotros know about how our brain develops and how it processes and regulates emotions, the more we can assist children with emotion processing bug. This knowledge also helps doctors to choose the well-nigh helpful treatment for these children. For example, if we know that a child struggles with recognizing an emotion, and so that is what we teach them to practice. Or if we run across that a child cannot control his emotions, we teach him ways to practise then. In the end, we want to sympathize and teach others how to deal with feelings of acrimony, fear, and aggression in a good mode. Nosotros hope that nosotros can aid those children struggling with their emotions and bring all of us a little closer to the "Jedi in u.s.."
Glossary
Emotions: ↑ Feelings, such as happiness, sadness, fear, acrimony, or joy.
Emotion Regulation: ↑ The process of adjusting, controlling, and adapting your own feelings depending on the background of a situation.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Photographic camera: ↑ A motorcar that allows researchers and doctors to take pictures of the inside of someone'southward body, such every bit bones, organs, or the brain.
Emotion Processing Network: ↑ All brain regions activated by emotions (feelings).
Meta-Assay: ↑ This is a study that takes the results of several studies nearly a certain subject and calculates the results based on all these studies combined together.
Funding
CS has received funding through FemNAT-CD, a collaborative project past the European Spousal relationship under the seventh Framework Program (grant understanding no. 602407). NR received funding through the Psychiatric University Clinics and the University of Basel.
Conflict of Interest Argument
The authors declare that the enquiry was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed every bit a potential conflict of interest.
References
[1] ↑ Gross, J. J., and Barrett, L. F. 2011. Emotion generation and emotion regulation: one or 2 depends on your indicate of view. Emot. Rev. 3:8–sixteen. doi:10.1177/1754073910380974
[2] ↑ Raschle, North. M., Lee, M., Buechler, R., Christodoulou, J. A., Chang, One thousand., Vakil, M., et al. 2009. Making MR imaging child's play – pediatric neuroimaging protocol, guidelines and procedure. J. Vis. Exp. doi:ten.3791/1309
[three] ↑ Phan, M. L., Wager, T., Taylor, S. F., and Liberzon, I. 2002. Functional neuroanatomy of emotion: a meta-assay of emotion activation studies in PET and fMRI. Neuroimage xvi:331–48. doi:10.1006/nimg.2002.1087
[4] ↑ Sterzer, P., Stadler, C., Poustka, F., and Kleinschmidt, A. 2007. A structural neural deficit in adolescents with conduct disorder and its association with lack of empathy. Neuroimage 37:335–42. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.043
[v] ↑ Raschle, N. M., Menks, W. Yard., Fehlbaum, L. V., Tshomba, East., and Stadler, C. 2015. Structural and functional alterations in correct dorsomedial prefrontal and left insular cortex co-localize in adolescents with aggressive behaviour: an ALE meta-analysis. PLoS Ane 10:e0136553. doi:x.1371/periodical.pone.0136553
What Part Of The Brain Controls Sadness,
Source: https://kids.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frym.2016.00016
Posted by: wetzelfooper.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Part Of The Brain Controls Sadness"
Post a Comment